introduction
In today’s technology-driven world, computers have become an essential part of our daily lives. But as devices get upgraded rapidly, millions of old desktops, laptops, and accessories are discarded every year, creating a growing challenge of electronic waste. This is where computer recycling plays a crucial role. Instead of sending outdated machines to landfills, recycling ensures that valuable parts are recovered, harmful materials are disposed of safely, and resources are given a second life.
Computer recycling is more than just disposing of old hardware—it is a structured process designed to protect the environment, conserve natural resources, and safeguard sensitive data stored in electronic devices. From secure data wiping and hard drive destruction to recovering metals like copper, aluminum, and gold, the recycling process minimizes waste while promoting sustainability.
For individuals, recycling offers a responsible way to clear unused gadgets. For businesses, it ensures compliance with data protection regulations and corporate sustainability goals. In this step-by-step guide, we will break down how computer recycling works, its environmental and economic benefits, and why it has become an essential practice in modern society.
What Is Computer Recycling?
What Is Computer Recycling? It is the process of safely collecting, dismantling, and reusing old computers and electronic parts instead of sending them to landfills. As technology changes quickly, millions of desktops, laptops, and accessories are thrown away each year, creating a large amount of electronic waste. Computer recycling ensures that reusable materials like copper, aluminum, plastic, and even valuable metals such as gold and silver are recovered and used again.
This practice is not just about reducing waste—it is also about protecting the environment and personal data. Many old devices still contain sensitive files on hard drives, so proper recycling includes secure data wiping or physical destruction. By doing so, it prevents identity theft and ensures compliance with data protection rules for businesses. Certified providers of hard drive destruction and shredding services in UK help organizations securely dispose of devices while meeting strict environmental and legal standards.
Why the Computer Recycling Process Is Important
In today’s fast-changing digital world, computers are upgraded and replaced more quickly than ever before. This constant cycle creates a massive amount of electronic waste, which can be harmful to the environment if not managed properly. This is where Computer Recycling becomes so important. Instead of allowing old desktops, laptops, and servers to end up in landfills, recycling ensures they are processed in a way that protects both people and the planet.
One of the key reasons for the importance of computer recycling is environmental protection. Computers contain hazardous substances such as mercury, lead, and cadmium. If these elements are left in landfills, they can leak into the soil and water, creating long-term health and ecological risks. Recycling helps prevent this by ensuring harmful materials are treated and disposed of safely.
Another vital factor is resource conservation. Computers are made of valuable metals like copper, gold, and aluminum. Recycling allows these materials to be recovered and reused in new products. This not only reduces the demand for mining but also saves energy and lowers carbon emissions.
Beyond environmental benefits, computer recycling also plays a major role in data security. Old devices often store sensitive information, and proper recycling includes secure data wiping or destruction. Many certified providers of IT Equipment Disposal Services in UK ensure that outdated desktops, laptops, and servers are handled responsibly, with hard drives securely wiped or destroyed. This keeps personal and business information safe from misuse while ensuring compliance with strict data protection regulations. In short, Computer Recycling is important because it addresses three major issues: reducing e-waste, conserving natural resources, and protecting data security—making it an essential practice for a sustainable future.
Step-by-Step Computer Recycling Process
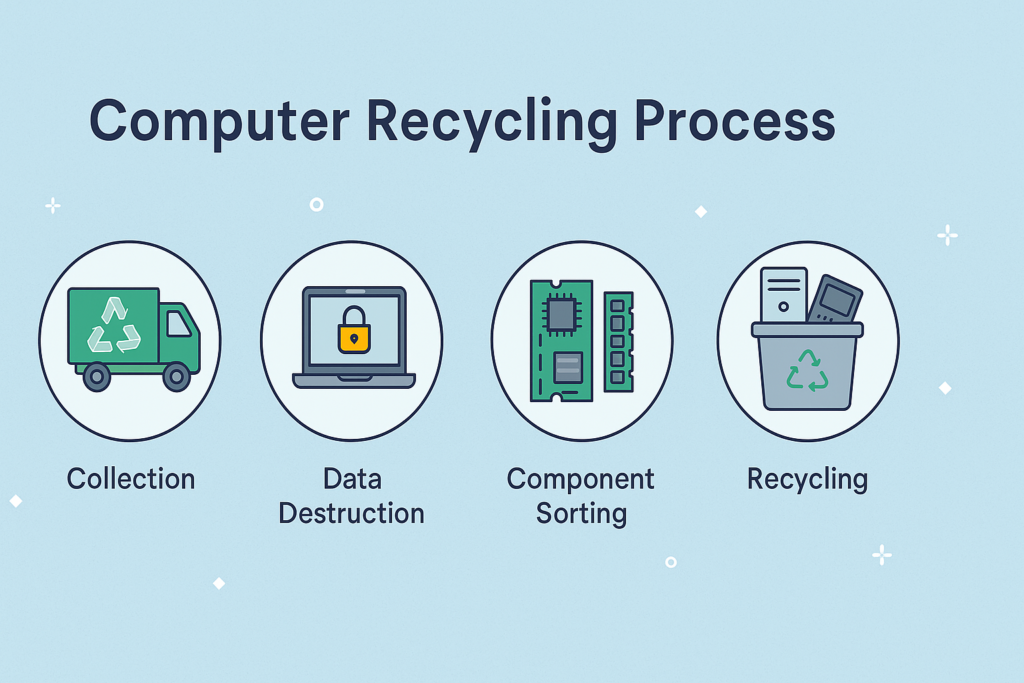
The Computer Recycling process is designed to safely handle old devices while maximizing the reuse of valuable materials. As technology evolves, millions of computers become outdated every year. Without recycling, these devices would add to the growing problem of e-waste, which poses risks to the environment and public health. A structured step-by-step process ensures that computers are not only disposed of responsibly but also contribute to sustainability.
The process begins with the collection and safe disposal of computers from households, schools, offices, and data centers. Once collected, the devices are sorted based on their condition. Functional parts like laptops and accessories may be refurbished, while non-working items are dismantled for recovery. Data security plays a vital role here, as old devices often contain sensitive information. Certified recyclers ensure hard drives are wiped or destroyed before further processing.
Next, materials such as metals, plastics, and glass are separated and sent for reuse in manufacturing. Components like processors, memory, and storage units may be refurbished for resale. Finally, reusable devices are repaired, tested, and reintroduced into the market, while remaining parts are recycled into raw materials.
By following this step-by-step process, Computer Recycling helps reduce waste, conserve natural resources, protect sensitive data, and promote a sustainable circular economy.
Computer Collection and Disposal
The first step in Computer Recycling is the collection and disposal of old devices. Computers are gathered from homes, schools, businesses, and organizations through recycling centers or pickup services. Some recycling programs even offer free collection, making it easier for people to responsibly discard their old machines.
Once collected, devices are transported to a certified facility where they are checked for condition and safety. Proper disposal ensures that harmful substances inside computers, such as mercury, lead, and cadmium, do not leak into the environment. Certified disposal services also issue documents that confirm devices are processed according to safety and legal standards.
This step is crucial because it ensures computers are not dumped into landfills where they can pollute soil and water. Instead, they enter the recycling chain, where every part is handled properly. Collection and disposal form the foundation of Computer Recycling, making it the first and most important step toward sustainable e-waste management.
Sorting and Laptop Recycling
After collection, the next stage in Computer Recycling is sorting. Computers are separated based on their condition, age, and type. Laptops, desktops, and servers are evaluated to see if they can be reused or refurbished. Devices that are still functional are set aside for repair and resale, while non-working units are dismantled for their materials.
Laptop recycling is especially important because these devices are widely used and often replaced more frequently. Recyclers test laptop components like batteries, keyboards, and screens to determine whether they can be reused. Working parts may be harvested and installed in refurbished systems, while damaged parts are sent for material recovery.
Sorting not only maximizes the number of usable parts but also ensures recycling is efficient and cost-effective. By separating devices early, recyclers save time and prevent unnecessary waste. In this way, Computer Recycling ensures that both laptops and other computers get a second life, reducing the strain on natural resources and the environment.
Data Wiping and Hard Drive Disposal
One of the most critical steps in Computer Recycling is data wiping and hard drive disposal. Old computers often contain personal or business information such as financial records, client files, and login details. If this data is not securely erased, it can lead to identity theft or data breaches.
Recyclers use advanced software to completely wipe hard drives, ensuring that no trace of data remains. In cases where data wiping is not possible, the hard drives are physically destroyed by shredding or crushing. This guarantees complete data protection before the recycling process continues.
Proper hard drive disposal also complies with privacy laws and regulations such as GDPR, making it essential for businesses handling sensitive information. By combining environmental responsibility with data security, this step strengthens the value of Computer Recycling. It ensures individuals and organizations can safely recycle their computers without risking exposure of their private information. For companies asking What Is IT Asset Disposal, it refers to the secure process of managing, recycling, or destroying old IT equipment in compliance with legal and environmental standards.
Component Recovery and PC Recycling
Once data has been securely handled, the Computer Recycling process moves to component recovery. At this stage, devices are dismantled, and individual parts are separated for reuse. Valuable materials like copper, aluminum, gold, and plastic are recovered and sent for further processing in manufacturing industries.
PC recycling also focuses on salvaging functional components such as processors, RAM, power supplies, and motherboards. Many of these parts can be refurbished and used in other computers, extending their life cycle. This reduces the need for producing entirely new components, saving both energy and resources.
Separating reusable components from non-reusable ones ensures recycling is efficient and sustainable. Hazardous substances like lead or mercury are carefully treated to prevent environmental harm. Overall, component recovery adds significant value to Computer Recycling, ensuring that old PCs are transformed into useful parts instead of waste, thereby supporting a circular economy.
Refurbishing Old Computers
The final step in Computer Recycling is refurbishing old computers. Not all devices need to be dismantled—some can be repaired and upgraded to work again. Recyclers test components like motherboards, processors, and storage units to see if they can be restored. If the computer passes quality checks, it is refurbished, repackaged, and sold at affordable prices.
Refurbished computers are especially valuable for schools, non-profits, and individuals who need cost-effective solutions. This step not only reduces waste but also makes technology more accessible to those with limited budgets. Refurbishing also extends the lifespan of devices, reducing the pressure on natural resources and minimizing e-waste generation.
By refurbishing, recyclers bridge the gap between disposal and reuse. It ensures that old machines can serve a new purpose instead of being discarded. This final stage makes Computer Recycling a complete process—one that protects the environment, conserves resources, and promotes affordable access to technology.
Related Post:- How to Dispose of Hard Drives Securely Before Recycling
Benefits of Computer Recycling
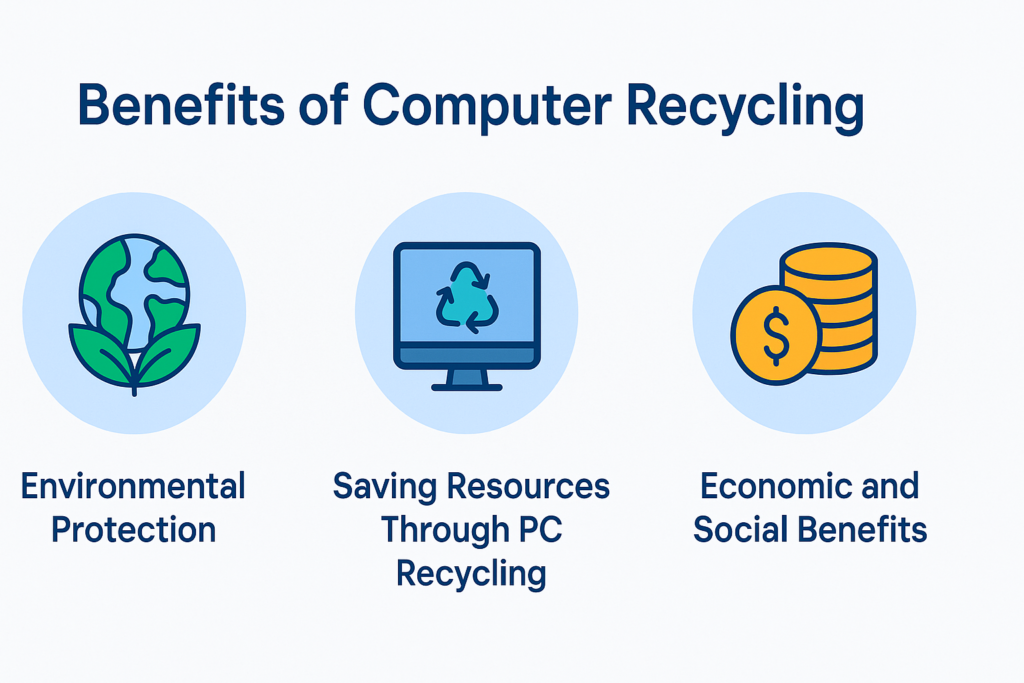
The benefits of computer recycling go far beyond simply clearing out old machines. It is a process that ensures technology is reused, resources are conserved, and harmful substances are managed safely. One of the most important aspects of recycling is secure hard drive disposal, which prevents data breaches by wiping or destroying sensitive information before parts are reused. This makes the recycling process not only eco-friendly but also safe for individuals and businesses.
Another key advantage is the opportunity for laptop recycling. Many laptops that are no longer in use still contain parts that can be repaired, refurbished, and sold again at affordable prices. This extends the lifespan of devices and makes technology more accessible to schools, non-profits, and individuals with limited budgets.
In addition, PC recycling allows for the recovery of valuable metals like copper, aluminum, and gold, reducing the need for new mining. By doing so, energy is conserved, and carbon emissions are lowered. Together, these practices support the circular economy, where resources are used more than once, reducing waste and promoting sustainability.
Overall, computer recycling delivers environmental, economic, and social benefits. It protects data, saves resources, and provides affordable access to technology—all while reducing the harmful impact of electronic waste on our planet.
Environmental Protection
A major benefit of computer recycling is environmental protection. Computers and laptops often contain hazardous substances such as mercury, lead, and cadmium. Without proper recycling, these substances can leak into the soil and water, harming both ecosystems and human health. Certified recycling ensures these materials are safely treated, while reusable parts are separated for further use.
Through PC recycling, valuable metals and plastics are recovered instead of being lost in landfills. This reduces the demand for extracting raw materials from the earth, which helps preserve forests, water sources, and natural habitats. Similarly, laptop recycling minimizes waste by giving devices a second life through refurbishment or repurposing.
Another critical aspect is hard drive disposal, which not only prevents sensitive information from falling into the wrong hands but also ensures that parts are processed in an environmentally safe way. By combining security with sustainability, computer recycling protects the environment while creating long-term ecological benefits.
Saving Resources Through PC Recycling
One of the most practical benefits of PC recycling is resource conservation. Computers are built with valuable metals such as copper, aluminum, and even small amounts of gold. Recycling allows these resources to be recovered and reused in new products, reducing the need for costly mining. This not only saves natural resources but also lowers the energy required for manufacturing.
Laptop recycling plays a similar role by salvaging batteries, screens, and processors that can be refurbished. Reusing these parts extends the life of existing devices and provides affordable options for consumers, schools, and organizations.
Equally important is hard drive disposal, which ensures data security before recycling begins. Once data is wiped or drives are destroyed, the materials can be reused without risk. By protecting information and reusing components, computer recycling helps industries save money, minimize waste, and promote sustainable development. It’s a win-win for both the economy and the environment.
Economic and Social Benefits
The economic and social benefits of computer recycling are significant. By refurbishing and reselling devices, laptop recycling makes technology affordable for students, small businesses, and non-profits. This helps bridge the digital divide by giving more people access to modern tools.
From an economic perspective, PC recycling creates opportunities in the recycling and refurbishment industry. Jobs are generated in collection, dismantling, and resale, boosting local economies. Additionally, the recovery of valuable metals reduces manufacturing costs for industries, making products more affordable in the long run.
On the security side, proper hard drive disposal ensures compliance with data protection laws. Businesses can recycle old equipment with confidence, knowing that sensitive information is safe. This builds trust and protects organizations from legal risks.
Socially, computer recycling also encourages responsible consumption and promotes awareness about sustainability. By choosing recycling, both individuals and companies contribute to a cleaner planet, resource efficiency, and fair access to technology for communities in need.
Challenges in the Computer Recycling Process
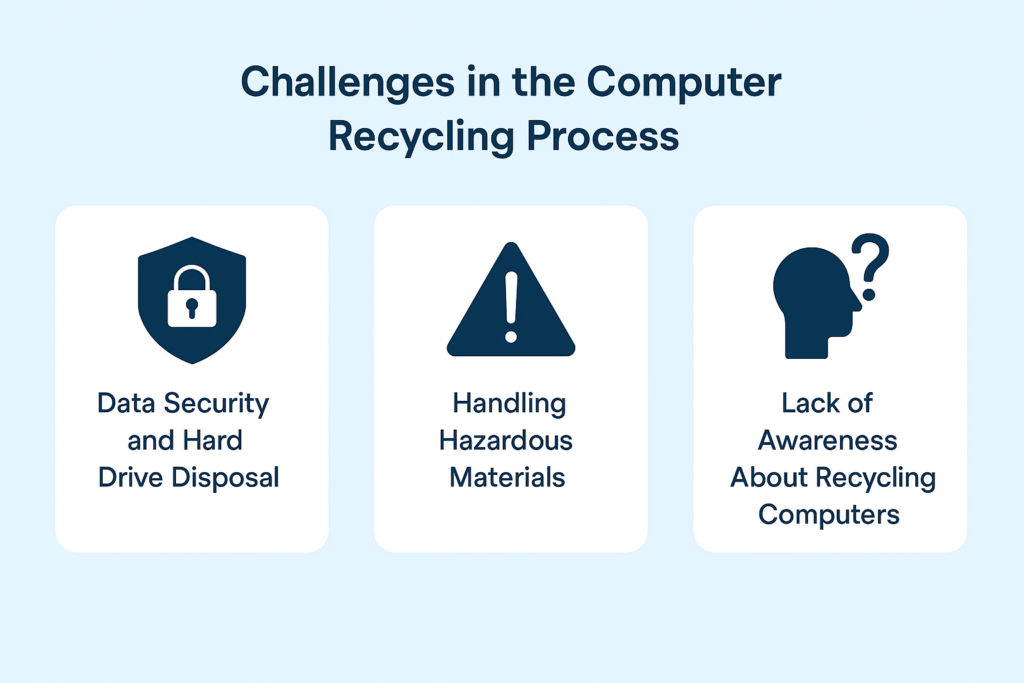
While Computer Recycling plays a vital role in reducing e-waste and protecting the environment, the process comes with its own set of challenges. One of the biggest concerns is data security. Old computers often store sensitive personal and business information, and without proper Hard Drive Disposal, there is a risk of data theft. Ensuring secure erasure or physical destruction of drives is an essential step, but not all recycling facilities follow strict standards.
Another challenge in the recycling process is the handling of hazardous materials. Computers contain toxic substances such as mercury, cadmium, and lead. If these are not managed properly, they can contaminate soil and water, posing serious risks to human health and the environment. Certified facilities are equipped to treat these materials safely, but many devices still end up in unregulated recycling channels.
A third challenge is lack of awareness. Many individuals and businesses are unaware of proper Computer Recycling options or assume that throwing devices in general waste is acceptable. This leads to higher volumes of e-waste in landfills and lost opportunities for resource recovery.
Addressing these challenges requires stricter regulations, better infrastructure, and increased public education. By ensuring safe Hard Drive Disposal, managing hazardous substances responsibly, and spreading awareness, the benefits of computer recycling can be maximized, supporting both sustainability and data security.
Data Security and Hard Drive Disposal
One of the most pressing challenges in Computer Recycling is data security. Every computer holds personal or confidential business information stored on hard drives. If devices are recycled without secure Hard Drive Disposal, sensitive data can be retrieved, leading to risks like identity theft or corporate data breaches.
To address this, certified recyclers use advanced data-wiping software to permanently erase information. In cases where erasure is not possible, physical destruction methods such as shredding or crushing are used to ensure drives cannot be accessed again. This not only protects individuals and organizations but also ensures compliance with data protection laws such as GDPR.
However, not all recycling facilities follow these strict practices, which increases the risk of data misuse. Public education and choosing certified services are key to solving this issue. Secure Hard Drive Disposal must remain a priority to make computer recycling safe and trustworthy for everyone.
Handling Hazardous Materials
Another major challenge in Computer Recycling is dealing with hazardous substances found in electronic devices. Computers often contain toxic materials such as mercury, cadmium, lead, and flame retardants. If these substances are not handled carefully, they can leak into soil and groundwater, causing long-term harm to human health and the environment.
Certified recycling facilities are designed to treat and separate these hazardous materials safely. For example, batteries and cathode-ray tubes require special processing to prevent contamination. Unfortunately, in many parts of the world, old computers still end up in informal recycling sectors where safety standards are ignored.
This improper handling leads to environmental damage and puts workers at risk. To overcome this challenge, stricter regulations, better monitoring, and investment in advanced recycling technologies are needed. Proper management of hazardous materials is essential to ensure that Computer Recycling truly contributes to sustainability rather than creating new health and ecological risks.
Lack of Awareness About Recycling Computers
A significant barrier to effective Computer Recycling is the lack of public awareness. Many individuals and even businesses are unaware that old devices can be recycled safely and securely. Some assume that throwing computers in regular trash is acceptable, while others do not know about certified recycling programs available in their area.
This lack of awareness not only increases e-waste in landfills but also wastes valuable opportunities to recover metals like copper, aluminum, and gold. It also leaves data security concerns unaddressed, as improper disposal often means hard drives are not securely destroyed.
Raising awareness is essential to solving this challenge. Governments, organizations, and recyclers need to educate people about the benefits of Computer Recycling and the importance of secure Hard Drive Disposal. Public campaigns, school programs, and corporate responsibility initiatives can encourage responsible recycling practices. With greater knowledge, more people will choose safe and sustainable options, reducing e-waste and supporting a circular economy. Many businesses also rely on Professional shredding services in London to ensure data is securely destroyed as part of responsible recycling.
Final Thoughts
As technology continues to evolve, computers are replaced faster than ever, leading to a sharp rise in e-waste. Understanding what is computer recycling? and following its step-by-step process is not only important but necessary in today’s digital world. From secure hard drive disposal to recovering valuable components and refurbishing usable machines, each stage of the recycling process ensures that old devices are handled responsibly and sustainably.
The benefits of computer recycling go far beyond waste reduction. It safeguards sensitive data, conserves precious resources like copper and aluminum, prevents hazardous materials from polluting the environment, and supports a circular economy where products are reused instead of discarded. At the same time, recycling creates economic opportunities by fueling refurbishment industries and providing affordable technology access to schools, non-profits, and individuals.
However, challenges such as lack of awareness, improper hard drive disposal, and unsafe handling of hazardous materials remain. Addressing these requires stricter regulations, stronger infrastructure, and increased education about recycling practices.
In conclusion, computer recycling is more than a disposal method—it is a responsible choice for protecting our planet, conserving resources, and ensuring a secure digital future. By recycling wisely, we contribute to a cleaner, safer, and more sustainable world.
FAQ
The computer recycling process involves several steps: collection, sorting, data wiping or hard drive disposal, dismantling, material recovery, and refurbishing. Old devices are first gathered and inspected for reusable components. Hard drives are securely erased or destroyed to protect data. Next, valuable materials like metals and plastics are separated for reuse, while hazardous substances are treated safely. Some computers are refurbished for resale, making the process both eco-friendly and resource-efficient.
Yes, laptops can be recycled just like desktops, though their components differ slightly. During laptop recycling, parts like batteries, screens, and keyboards are carefully dismantled. Valuable materials such as aluminum and copper are recovered, while batteries are processed separately due to their chemical content. Functional parts like RAM or processors may be reused in refurbished systems. Proper laptop recycling ensures fewer devices end up in landfills and maximizes the reuse of valuable components.
Data safety is ensured through certified hard drive disposal. Before recycling begins, recyclers use advanced software to completely wipe hard drives. If wiping is not possible, drives are physically destroyed by shredding or crushing. This guarantees no sensitive data can be accessed. Certified recyclers often provide certificates of destruction to confirm compliance with data protection laws, ensuring businesses and individuals can recycle computers without risk of data leaks or identity theft.
Many parts of a computer can be recycled, including hard drives, processors, motherboards, power supplies, and RAM. External components such as keyboards, mice, and monitors are also recyclable. Valuable metals like gold, copper, and aluminum are recovered from internal parts. Plastics and glass are separated for reuse in new products. Even non-working components may be dismantled to recover materials. Recycling maximizes resource use while reducing waste and protecting the environment.
Computer recycling prevents hazardous substances like lead, cadmium, and mercury from entering the environment. It reduces pollution of soil and water and lowers greenhouse gas emissions by minimizing the need for manufacturing new materials. Recycling also conserves natural resources by recovering metals and plastics from old devices. Additionally, refurbishing computers extends their lifespan, reducing demand for new production. These steps make computer recycling a critical part of promoting sustainability and environmental protection.
Computer disposal usually refers to throwing devices into general waste, which often ends up in landfills. This method is unsafe because it pollutes the environment and leaves data vulnerable. In contrast, computer recycling is a structured process that dismantles, recovers, and reuses valuable components while ensuring secure hard drive disposal. Recycling is sustainable and safer for the environment, while disposal is often harmful. Choosing recycling means protecting both the planet and your personal data.
Yes, hard drives can be recycled separately, but they must go through secure hard drive disposal first. This includes data wiping or physical destruction to ensure no information remains accessible. After data removal, materials like aluminum, steel, and circuit boards inside the hard drive are recovered for reuse. Certified recycling centers handle this process safely, reducing environmental impact and ensuring compliance with data protection laws. This makes hard drive recycling both safe and eco-friendly.
Computer recycling supports the circular economy by ensuring old devices and materials are reused instead of wasted. Valuable resources like copper, aluminum, and plastics are recovered and fed back into production cycles, reducing the need for raw materials. Refurbished computers extend product lifespans, while secure hard drive disposal ensures safe reuse. This closed-loop system minimizes environmental impact, lowers energy use, and makes technology more sustainable. Recycling transforms waste into resources, powering a greener economy.